Sign up for Lesson Plans, discounts & more!
Igneous, Metamorphic, and Sedimentary Rock Gallery

The Rock Gallery contains pictures and descriptions of common igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. The igneous rocks, like the granite that makes up half Dome, in Yosemite National Park, pictured above, are listed at the top of
the page followed by metamorphic rocks. The sedimentary rocks are at
the bottom of the page. The names of each of the rocks pictured are links to more information about that type of rock .
The following are examples of igneous rocks. It is not an all inclusive list but a brief pictorial list of some common igneous rocks.
Examples of Common Igneous Rocks |
|
 |
Andesite is a gray to black volcanic rock. It is generally erupted from stratovolcanoes as thick lava flows. It can also generate strong explosive eruptions to form pyroclastic flows. |
 |
Basalt - Basalt is a hard, black volcanic rock. Less than ½ of the weight of basalt is silica (SiO2). Because of basalt's low silica content, it has a low viscosity (resistance to flow). This enables basaltic lava to flow quickly and allows volcanic gases to escape without explosive events. |
 |
Dacite lava is most often light gray, but can be dark gray to black. It is one of the most common rock types associated with enormous Plinian-style eruptions. |
 |
Pumice is light and porous. It forms during explosive eruptions. Pumice is full of holes caused by expanding volcanic gases. It is composed of volcanic glass and minerals, and can form in all types of magma: basalt, andesite, dacite, and rhyolite. |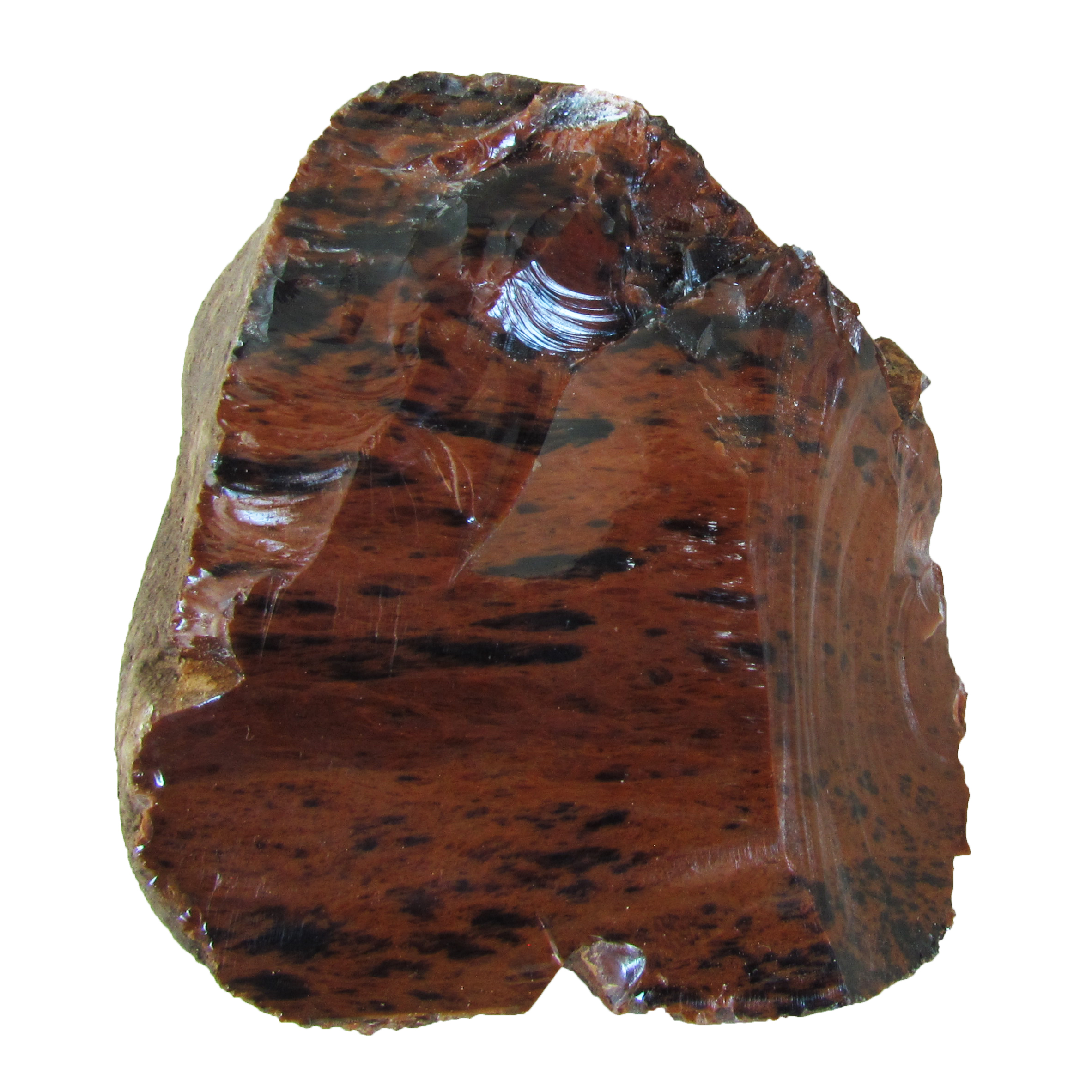  |
Obsidian is usually black in color though it can also be red or have a greenish tint. It is a dense volcanic glass, usually composed of rhyolite, rich in iron and magnesium. Obsidian is formed when the lava cools so quickly that crystals do not have time to grow. Obsidian fractures with very sharp edges. It was used by Stone Age cultures for making knives, arrowheads, and other tools where sharp edges are important. |
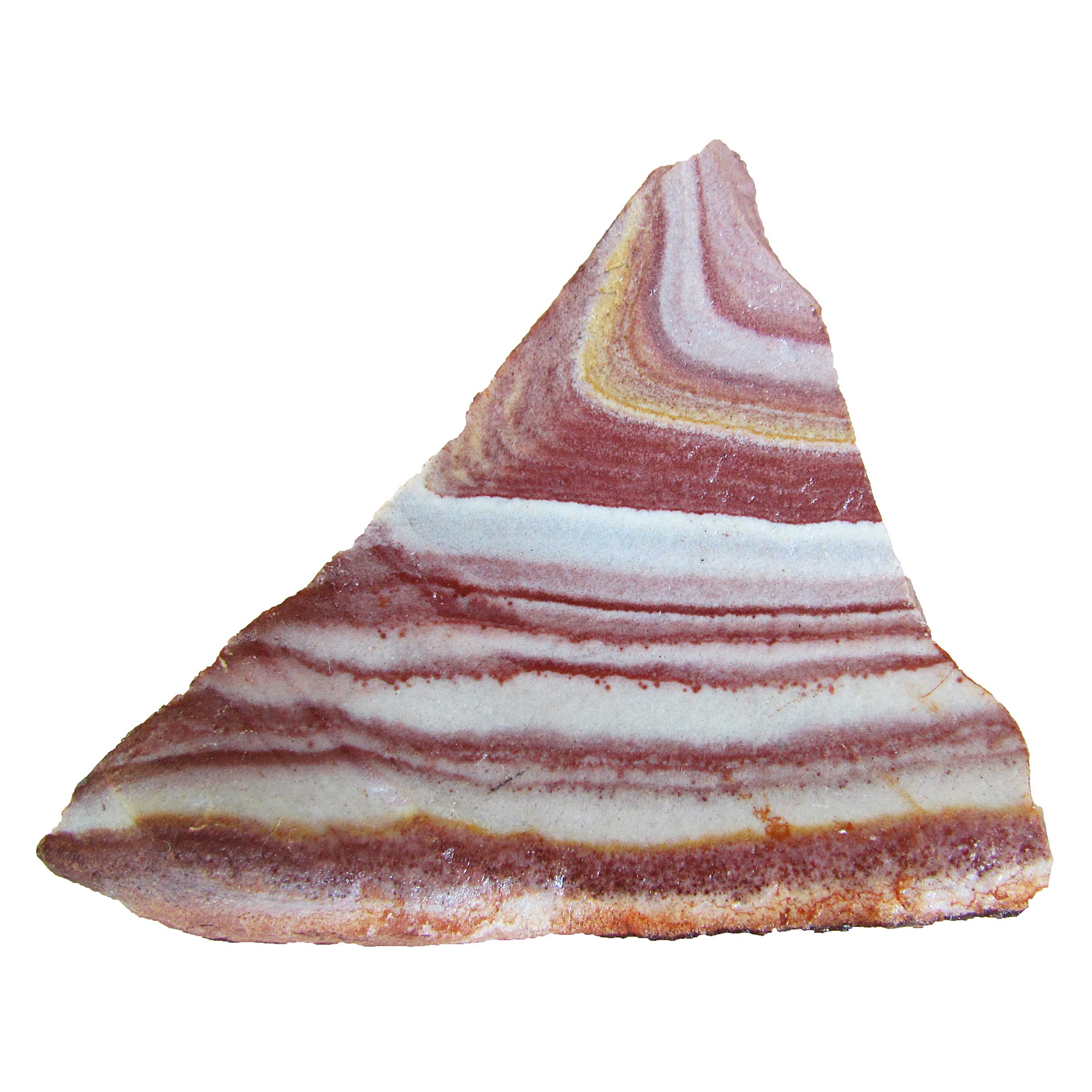 |
Rhyolite is a light-colored volcanic rock. It has a high silica content which makes it very viscous. This prevents gases from escaping causing rhyolite eruptions to be explosive. |
 |
Granite is a common intrusive plutonic igneous rock. Because it cools slowly crystals have time to form. The name granite comes from the Latin word granum which means “a grain” for the coarse grain crystalline structure of the rock. |
Examples of Common Metamorphic Rocks |
|
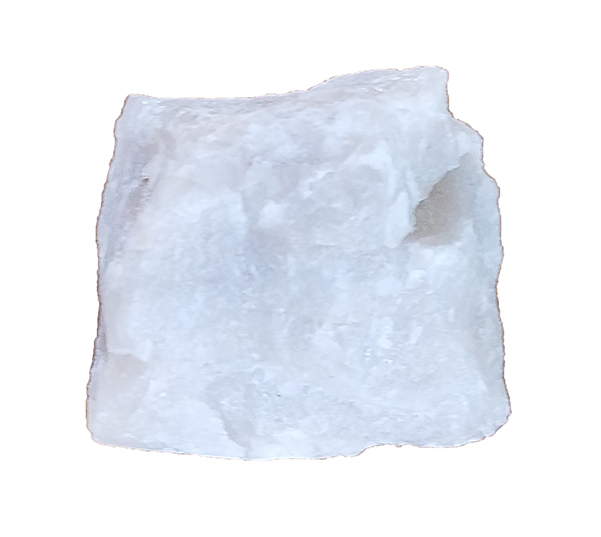 |
Quartzite is a coarse-grained metamorphic rock derived from sandstone. |
 |
Marble is a metamorphic rock that comes from metamorphosed limestone or dolomite. |
 |
Slate is a fined grained metamorphic rock. |
 |
Phyllite is a fined grained metamorphic rock. |
 |
Schist is a course grained metamorphic rock. |
 |
Gneiss is a medium to course grained metamorphic rock. |
Examples of Clastic Sedimentary Rocks |
|
 |
Conglomerate is made up of rounded pebbles cemented together. |
 |
Breccia is made up of angular pebbles cemented together. |
 |
Limestone is calcium carbonate deposited by the shells of once living creatures or from the residue of water.. |
 |
Sandstone is sand grains cemented together into solid stone. |
 |
Siltstone is made from silt particles cemented together. |
 |
Shale is made from silt particles cemented together. It is similar to siltstone but with even finer grain size. |
 |
Banded Ironstone is a sedimentary rock made of layers of iron oxides and iron poor chert. |
Igneous metamorphic sedimentary rock are the three main types of rock on earth. Read more about Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary Rock:
Igneous Rocks
Metamorphic Rocks
Sedimentary Rocks
 |
 |
 |

INTERESTED IN MORE? IF SO, YOU MAY WANT TO CHECK OUT OUR OTHER SITES:
fossilicious.com - Our online fossil and mineral rock shop.
fossils-facts-and-finds.com - An educational site about fossils.