Sign up for Lesson Plans, discounts & more!
Halite
The Indispensible Mineral

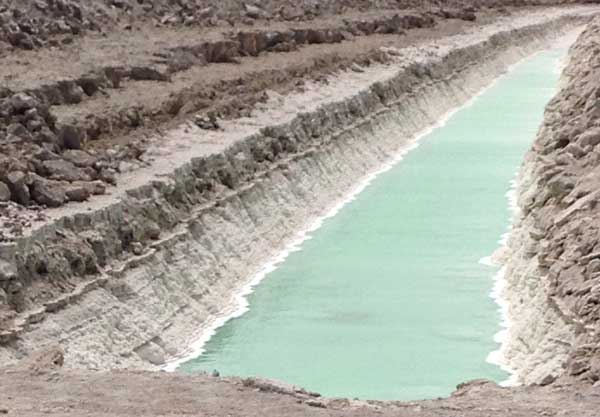
Halite is also known as rock salt. The chemical name is sodium chloride NaCl It is called an evaporate. It forms in places where sea water has been isolated from the ocean forming a lake. As the saltwater evaporates in the lake the salt becomes concentrated in the remaining water. As the water continues to evaporate the lake can no longer hold the same amount of salt. The salt precipitates out and is deposited as crystallized sodium chloride or salt.
Surface Deposits
There are two areas in the United States where rock salt is currently
being deposited naturally, The Great Salt Lake in Utah and Searles Lake in
California. The Great Salt Lake is the remains of a vast inland sea that
has left salt deposits over much of North West Utah. California also has some man made salt operations. You can read more about that here. Evaporate Sedimentary Halite Deposits.
Underground Deposits
There are many places on earth where salt water lakes have been
deposited in the past. Some of these deposits can be 400 meters thick!
Some of these underground deposits are being mined for salt.
Description
Halite normally forms perfect cubes, look at ordinary table salt with a magnifying glass.
Rock salt can be clear or have a pink cast to it. The pink color comes from bacterial debris that has been trapped in the salt crystals.
The easy way to identify sodium chloride is by taste. First lick your finger, then touch the mineral in question, finally taste your finger. If it tastes salty it is halite. Never lick a specimen for the taste test! There are poisonous minerals that resemble halite. By using your finger you can keep yourself safe.
Halite has an unusual property called deliquescence. Deliquescence means that halite readily combines with water. A halite specimen will absorb moisture from the air sometimes leaving a powdery white residue. Halite will dissolve in water.
Uses
Halite has many uses. We get our table salt from it. In cold climates
salt is used to control ice on roads and sidewalks. It is used to soften
water and as an ore for sodium and chlorine.
Mineral Properties
Chemical formula: NaCl sodium chloride
Color(s) : Clear to white; can be pink, blue, purple, gray, or yellow
Streak: White
Luster: vitreous
Transparency: Transparent to translucent
Crystal system: isometric
Crystal Habit: cubes can be massive, granular or fibrous
Specific Gravity: 2.1
Hardness (Mohs): 2
Cleavage: perfect in 3 directions
Fracture: conchoidal
Other Characteristics: salty taste
Uses: food supplement, ice control, water softening, ore for sodium and chlorine
Location: Great Salt Lake, Utah, Searles lake, California in the USA, Germany, France

INTERESTED IN MORE? IF SO, YOU MAY WANT TO CHECK OUT OUR OTHER SITES:
fossilicious.com - Our online fossil and mineral rock shop.
fossils-facts-and-finds.com - An educational site about fossils.